<br>
##Sensing with Step Response (transmit-receive, or tx-rx)
- [Arduino sketch for tx_rx](./tx_rx01.txt) Single measurement.
- [Arduino sketch for tx_rx](./rx_tx02.txt) Average of N points. Has the algorithm built into the loop function.
- [Arduino sketch with function for tx_rx](./rx_tx03.txt) Has the algorithm in a separate function, to make coding easier.
- Here's how it works:
- transmit (tx) pin is made alternately high (5V or 3.3V) and low (0V). Note that the figures show the number for 5V boards. For 3V boards (like the ATSAM-based Adafruit boards) the highes voltgae is 3.3V.
- This charges and discharges the tx electrode.
- On the rx electrode there is a small 'blip' up or down as the tx pin toggles.
- These blips are measured by the Arduino analog input (ADC), and "low" subracted from "high" (see figure).
- This result varies depending on how closely the two plates are coupled by the electric field. It increases as the distance decreases and also
changes with the amount of overlap and the material between the plates.
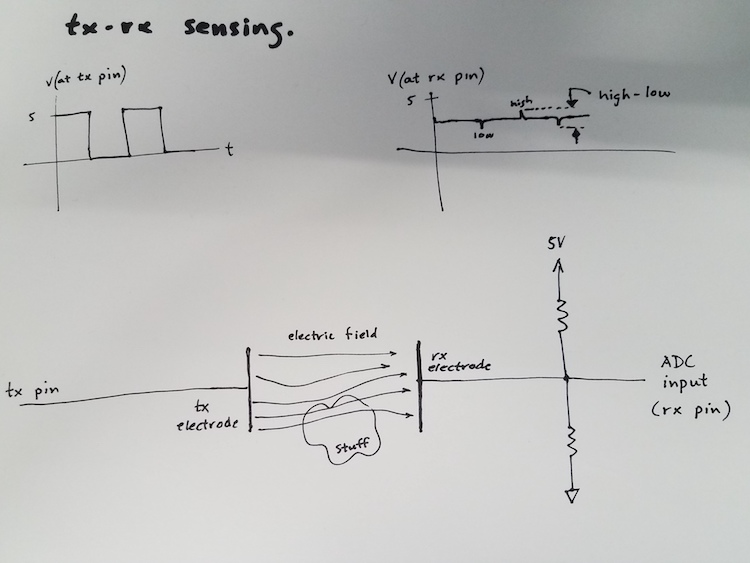
Above is a sketch of the setup for tx-rx sensing. The (optional) resistors between 5V(3.3V) and GND make the signal stabler. The input
to the ADC is attached to the point halfway betwen 5V(3.3V) and ground, and is therefore at 2.5(1.2) volts, except for the transient blips that occur at the tx electrode changes voltage. These resistors should be equal, and should have values of 1 mega-ohm or larger.
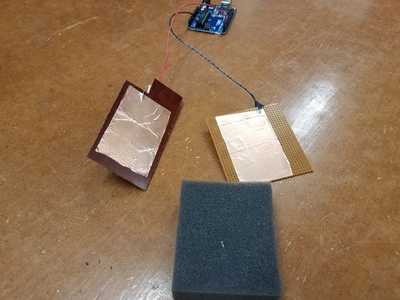
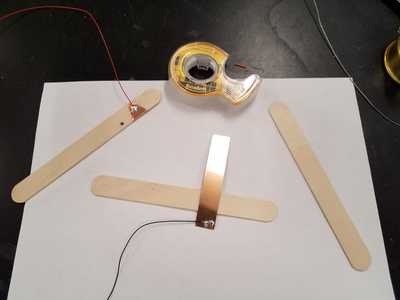
Below are pictures of two copper electrodes (tape on circuitboard material) attached with
no extra resistors to pin4 and A0 of the Arduino. Left, the plates. Middle, the plates with foam between.
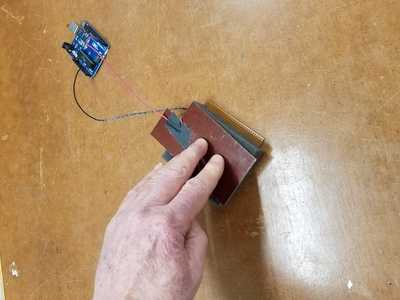
Right, the plates get closer together (and the signal increases) when force is applied. Force Sensor!

---
###Several ways to use tx-rx as sensors.
- Proximity between two electrodes lets you measure force through changes in position.
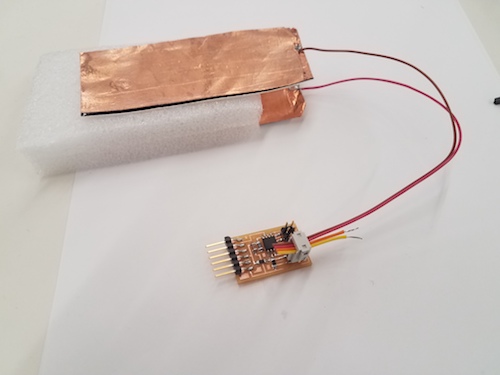
- Wedge geometry as a multi-use sensor.
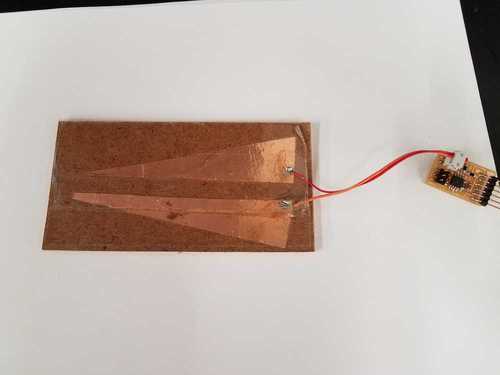
- Tilt sensor. Bottle partially filed with water.

- Pipetter liquid sensor.

- A crude rotary sensor.
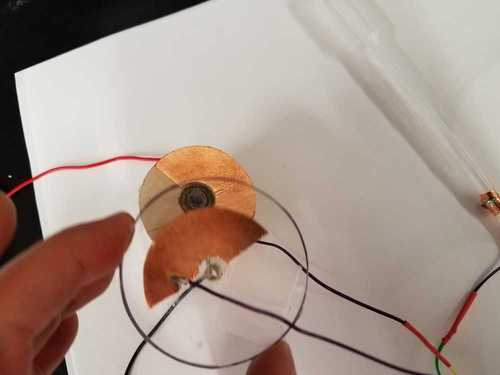
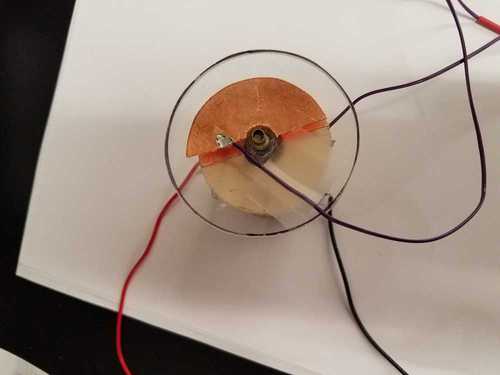
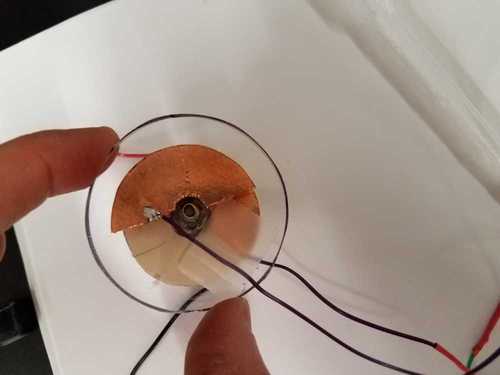
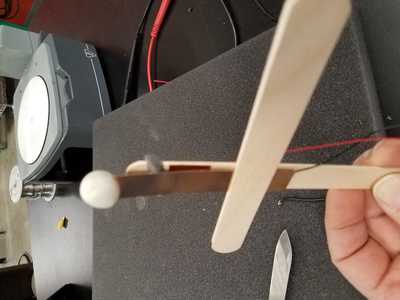
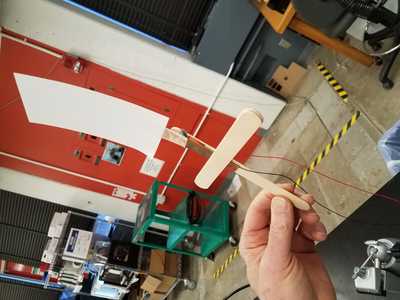
- A popsicle stick arrangment used as accelerometer and wind sensor.
---